Can Marine Algae Change with the Climate?
show/hide words to know
What’s in the Story?
You’re doing your homework and your stomach starts to rumble. You make your way to the kitchen to make a delicious grilled-cheese sandwich. You grab two slices of bread, cheese from the refrigerator, heat up the stove and prepare a delicious meal. Ahhh, now you feel great and can continue with your school work.

The intertidal zone is the area along a body of water that is exposed for part of the day during low tide. Image by Hugh Chevallier.
Algae living in the intertidal zone get hungry too. They are able to make their own food by combining light from the sun with carbon dioxide and water. This process is called photosynthesis. And just like you, algae need the energy to survive.
While the amount of sunlight available can affect photosynthesis, other conditions can also change how much energy algae can make. For example, the amount of carbon dioxide in the environment can change how much food algae can make. This is one way that climate change can affect algae.
In the PLOS ONE article, “Effects of Ocean Acidification and Temperature Increases on the Photosynthesis of Tropical Reef Calcified Macroalgae(link is external),” scientists studied how climate change could affect algae living in marine ecosystems.
Preventing Ocean Acidification
Algae are important in marine environments. They are at the bottom of the food chain, meaning many ocean creatures eat algae as their main source of food. To get the energy algae need to survive, they use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Yet, too much carbon dioxide in the ocean causes the water to become acidic, a process called ocean acidification. This could be very harmful to algae and other ocean creatures.

Some algae can help balance ocean acidification, by removing carbon dioxide from the water. Image by FalsePerc.
It’s important to understand how these changes affect algae, because some algae help balance ocean acidification. Algae can release enzymes into the water that can help quickly break down carbon dioxide into bicarbonate ions. The algae can then take up these bicarbonate ions and use them for photosynthesis and calcification. Calcification is the buildup of calcium carbonate (what shells are made of). This material allows these algae to have a hard texture, resembling a rock. This is why the algae can be called ‘calcifying’, because they are able to produce calcium carbonate from bicarbonate.
Removing bicarbonate from the water helps the water stay neutral and avoid becoming acidic. If there is not enough of these enzymes around to turn carbon dioxide into bicarbonate, there will be more carbon dioxide in the water and the water will become acidic.
Climate and Carbon Dioxide
Climate change is causing carbon dioxide levels and the temperature of Earth to go up. Scientists predict ocean acidification and higher temperatures will be a problem for marine ecosystems in the future. An important step to understanding this problem is to know how algae may react to the expected changes.

One of the species the scientists tested is quite similar to this species of calcifying macroalgae (Halimeda copiosa). Image by NOAA.
Scientists looked at different species of tropical calcifying macroalgae (“macro” means large). The scientists performed two experiments. The first experiment looked at how an increase in carbon dioxide affects photosynthesis. The second experiment looked at the effect of a higher water temperature on the rate of photosynthesis in the algae.
Carbon Dioxide: How Much is Too Much?
Scientists wanted to know how different species of macroalgae responded to an increase in carbon dioxide. They grew algae in tanks in which they could control the conditions of the water. They used four different treatment groups of varying carbon dioxide levels for each species, with four tanks tested per group.
One group had the same level of carbon dioxide that is currently in the ocean. Two groups had increasing levels of carbon dioxide that are expected to be reached in the ocean in the next 50 to 100 years. One final group was treated with water more acidic than future predictions of ocean acidity.
In all tanks, the scientists measured how much of the calcifying enzyme the macroalgae produced. They also measured how these conditions affected efficiency of photosynthesis.
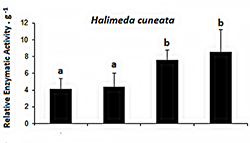
Only one species (Halimeda cuneata) made more enzyme when exposed to higher levels of carbon dioxide. This helped reduce acidity of the water. The only algae that showed a change in photosynthetic efficiency was the group exposed to the highest level of carbon dioxide. This shows the predicted increase in carbon dioxide levels for the future may not have a huge impact on the amount of energy these algae species produce.
It’s Getting Hot in Here Now
To determine if an increase in temperature affects photosynthesis in algae, scientists treated four groups with different water temperatures. One tank had the same temperature as the current water temperature in the ocean and was used as the control to compare the other tanks to. Three other groups of tanks had temperatures that were up to 4.5˚C higher than the current ocean water temperature. The scientists measured photosynthetic efficiency 4, 11, and 15 days after the experiment started.
Although these temperature increases do not seem high, they can make a huge difference to anything that lives in these waters. Imagine it’s a hot day and you’re studying for a test when the air conditioner stops working. At first, it does not affect your ability to study. But as the temperature increases by a degree or two, it can cause you to start sweating and slowly lose focus on what you are studying. If ocean temperatures increase too much, the algae will likely be affected.
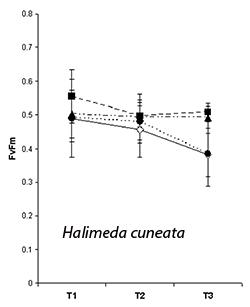
Scientists found a one-degree increase in temperature caused a slight increase in photosynthetic efficiency of one algae species (Halimeda cuneate) at one time point. Temperatures higher than this did not affect photosynthetic efficiency. As the temperature of ocean water increases, it does not mean algae will consume more carbon dioxide. Some species will likely produce the same amount of energy from photosynthesis, regardless of the temperature increase.
The Fate of Calcifying Algae
Some species of calcifying algae are not doomed with climate change. Imagine the algae that live on the part of the beach right along the water. Sometimes they are covered in water, other times they are exposed to the air. They are used to experiencing change in their environment. This may make these algae better at adapting (or changing between generations) to future conditions.
These experiments showed that, independently, temperature or acidic conditions expected with climate change did not harm these algae. Despite increased temperature or increased carbon dioxide, these algae species still made enough energy to survive. This means there may be hope for some species of algae. However, not all species of algae are this lucky, and many may be affected more seriously by climate change.
Additional images via Wikimedia Commons. Curled Mesophyllum coralline algae thumbnail image and red calcifying algae image by Philippe Bourjon.
View Citation

Some algae are called calcifying algae, because they create hard crusts out of calcium carbonate. These algae are important to reducing ocean acidification. But if temperatures and acidity start to rise, will these algae be able to survive?
Learn more about life in the sea by visiting the marine biome.
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.