- Ask A Biologist
- Biology Bits
- Bird Finder
- Body Depot
- Coloring Pages
- Experiments and Activities
- Virtual Pocket Seed Viewer
- Air Pollution
- Catch and Sketch Plankton
- Composting
- Cutting Out Brain Tumors
- Experiment Overview
- Heavy Water
- How Do Animals Grow?
- Hummingbird Lunch
- It’s a Plankton Eat Plankton World
- Let the Germs Begin
- Life of the Leafcutter
- Nerve Experiment
- Seasoned to the Tilt
- Seeing DNA
- Sooty Selection
- Virtual Seed Experiment
- When Water Gets Icy
- Your Dog's Personality
- Breaking Proteins
- Managing Mosquitoes
- Mysterious World of Dr. Biology
- Games and Simulations
- How To
- Puzzles
- Quizzes
- ABC Vitamins
- Ant Anatomy
- Ant Farm
- Ants
- Bats
- Bees
- Beetles
- Birds, Hormones, and Seasons
- Building Blocks of Life
- Butterfly Vision
- Cloning
- Collecting Ants
- Color Vision
- Crazy Climate
- Desert Biome
- Digging Bees
- Ecosystems
- Endangered Species
- Feathers
- Fig Wasps
- Freshwater Biome
- Genetics and Mendel
- Grasslands Biome
- How Vision Works
- Kazakhstan
- Lizards
- Mapping the Future
- Medicinal Plants
- Metamorphosis
- Monarchs
- Nervous System
- Plankton
- Pollen
- Python Parenting
- Salamanders
- Savanna Biome
- Scientific Method
- Scorpions
- Sea Urchins
- Searching the Internet
- Seeds
- Snacking on Sunlight Quiz
- Space Physiology
- Superorganisms
- Taiga Quiz
- Taxonomy
- Temperate Biome
- Tropical Rainforest Biome
- True Bugs
- Tundra Biome
- Two Headed Snake
- What's a GMO?
- Whats a biologist?
- X-ray Crystallography
- Quizzes in Other Languages
- Az élet építőkövei - Kviz
- Bichos Verdaderos
- Biologia de las Plumas
- Biome tempéré
- Bloques de Construcción de la Vida
- Cayendo en agua dulce
- Comiendo la Luz del Sol Examen
- Comment voit-on?
- Comprendre Les Paries Le Quiz
- De Quiz
- De Quiz
- Denevérek
- Ecosystema el Examen
- Erizos de mar
- Explorons La Toundra
- Fotossíntese Questionário
- Fotosynthese Quiz
- Het Examen
- La Vita Nello Spazio Quiz
- Lagarto Concurso
- Le Quiz
- Le Quiz de la Savane
- Les Chauves-souris
- Les Coléoptères
- Les Oursins
- Les Scorpions
- Les invisibles du monde aquatique
- Les plumes
- Les écosystèmes!
- Les éléments de construction de la vie
- Los Escorpiones
- Metamorfosis
- Monarcas Migratorias Examen
- O Călătorie Nervoasă Test
- Papillons Monarques
- Pastizales-TEST
- Provim i shpejtë
- Prueba Tundra
- Quiz cellulare
- Sabana el Examen
- Taiga Biome Le Quiz
- Test de vision des couleurs
- Un Viaje Nervioso, El Examen
- Vleermuisvoedsel Examen
- ¡Los escarabajos!
- ¡Semillas!
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- World of Biology
- Ants
- Nanoparticles - A Matter of Scale
- Bats
- Fig Wasps
- Ant Farm
- Cloning Ewe
- Building Blocks of Life
- Collecting Ants
- Did You Know Butterflies Are Legally Blind?
- Face to Face with Ants
- Feather Biology
- He Ain't Tasty, He's My Brother
- How Do Beetles Reproduce?
- How to Find What You Need on the Internet
- I Spy an Ecosystem
- Mighty Morphing Tree Lizards
- Migrating Monarch Butterflies
- Mite Mighty Foe to 'Killer' Bees
- Not So Scary Scorpions
- Pollen - Nature's Tiny Clues
- Sea Urchins Do Research
- Secrets of a Superorganism
- Seeing Color
- Time Traveling Plants
- Two-Headed Snake
- Using the Scientific Method to Solve Mysteries
- Where in the World Is Kazakhstan?
- Why Are English Sailors Called Limeys?
- A Nervous Journey
- A Walk in the Park
- An Invisible Watery World
- Anatomy of an Article
- Antibiotics vs Bacteria: An Evolutionary Battle
- Bee Bonanza
- Bee Jeweled
- Big BIG Bugs
- Big Bad Beetles
- Biology's Beginnings
- Birds and Their Songs
- Boundless Biomes
- Cells Living in Cells
- Contemplating the Coasts
- Controlling Genes
- Crazy Climate and Wacky Weather
- Cutting DNA with CRISPR
- DNA Basics
- Darwin and Mendel Talk
- Delving into Deserts
- Desert Diggers
- All About Mosquitoes
- Are Wildfires Bad?
- Changing Life in the Arctic
- Desert Fruits Rock
- Growing Cells
- Keeping up With Kangaroos
- Rising Cicadas
- Searching for Alien Life
- Spotting Science Lies
- Using Research to Learn The Truth
- Vaccine Science
- What Is Fake News?
- Why Do Mosquitoes Like Me?
- Earth Day All Year
- Exercise for Your brain
- Falling into Freshwater
- Focusing on Physiology
- Frozen Life
- Glow-in-the-dark Plants
- Grasping Grasslands
- Hardy Gilas
- How Do We Hear?
- How Do We See?
- How Do We Sense Smell?
- How Do We Sense Taste?
- How Do We Sense Touch?
- Hummingbirds
- Indiana Jane
- Itty Bitty Beasts
- Linnaeus and the World of Taxonomy
- Making Life Crystal Clear
- Making the List
- Mapping the Future
- Marveling at the Marine Biomes
- Metamorphosis: Nature’s Ultimate Transformer
- Nanobiotechnology: Nature's Tiny Machines
- Nature's Colors of Love
- Nature's Medicine
- Observing the Open Ocean
- Ouch - Body Defense and Repair
- Parts of the Nervous System
- Perfect Python Parenting
- Phosphate Fix
- Puzzling Pathogens
- Searching the Savanna
- Secrets of Sleep
- Sensing the World
- Singing in the Rain
- Six-legged Recipes
- Snacking on Sunlight
- Solving a Genetic Mystery
- Sonoran CSI
- Spaced Out Physiology
- Switching of Seasons
- Taking Care of Nature
- Taking in the Temperate Forest
- The Peppered Moth: A Seasoned Survivor
- To Breed or Not to Breed
- Tough, Tiny Tiger Beetles
- Trailing Through Taiga
- Trekking through Tundra
- Tropical Rainforest
- True Bugs
- Using Animals in Research
- Vitamins: Vital or Not?
- What is Evolutionary Medicine?
- What's a Biologist?
- What's a GMO?
- What's a Genome?
- Where the Rewilded Things Are
- Meet Our Biologists
- Angelic Creature With Devilish Charm
- Battling Bacteria that Break the Body
- Bee Movie Maker
- Breeding Birds and Beyond
- Chasing Tiny Tigers
- Colorful Partners
- Cow Pies, Termites - A Main Attraction
- Crusty Microbiologist
- Getting to the Root of Plant Biology
- He Knows a Good Egg When He Sees One
- Hot Research
- Insect Fashion Show
- Keying in on Keystone Species
- Learning to Remember
- On the Lookout for Locusts
- Panama Kate
- Smashing Success
- Studying Monster DNA
- The Interest of Insects
- Tobacco's Wild Ride
- What Lies Beneath
- Building at a Nanoscale
- Cooperation or Conflict?
- Hunting for Hidden Viruses
- Mending with Microbes
- Treating Cancer with a Rabbit Trick
- Keys to the Coronavirus
- Smarter Ways to Battle Bacteria
- Breaking Cell Boundaries
- Catching Body Invaders
- Detect and Protect
- Fighting Brain Disease
- Looking for Life
- Manipulating Microbes
- Mutations Matter
- Peeking Into Ant-Plant Pacts
- Secrets in Sewers
- The World Inside You
- What's in Our Water?
- Listen and Watch
- A Walk on the Wild Side
- A visit to NSF
- About Bees and the Bee Genome
- Ant Farm
- Ant Life Part 1
- Ant Life Part 2
- Ant Math
- Art & Science of Broadcast Journalism
- Bats, Bones, and Biology
- Bee Movie Maker
- Been There, Dung That
- Biology Business
- Biology Net
- Birds of a Feather
- Breath of Fresh Ocean Air
- Bugs in Films
- Bugs in Space
- Build Your Own Ant Farm (Part 1)
- Build Your Own Ant Farm (Part 2)
- Butterflies and Insect Vision
- Casting a Podcast Line
- Cataglyphis
- Cell CAT Scans
- Collecting Ice Cores
- Cute Colorful Poison Dart Frogs and Their Mimics
- Cybertaxonomy
- Dear Aliens
- Desert Plants
- Dr. Biology Goes to Washington DC: Science for Everyone
- Dr. Biology Visits the Laboratory of Michael Angilletta
- Dr. Biology visits with Biologist Kate Ihle
- Drawn to Bones
- Ed Wilson 1
- Ed Wilson 2
- Evolution of Bird Flight
- Feather Biology
- Fire and Life
- Food for Thought About GMOs
- Cells and Cancer
- Hacking Nature
- Healing with clay
- Hiking South Mountain Park
- Hulking Biology
- Inner Space the Final Frontier
- Insect Infatuation
- Iridescence
- Jaguar in My Backyard?
- Keeping Cool
- Keystone Species
- A Matter of Trust
- A Tasty Bite of Science
- Adventures of a Zoo Veterinarian
- An AI Conversation
- Are Plants Made from Thin Air?
- Beetle Mania
- Biology Explained by Cats
- Blood-Sucking Science Mystery
- Breathtaking Biology – a metabolome adventure
- Bringing Biodiversity to the City
- Can't Live Without You
- Capturing Curious Minds: Communicating Complex Science
- Charting the Mysteries of the Mind - Unraveling Alzheimer's and Dementia
- Chronicles of a Zookeeper
- Drylands, Hot Topic
- From Cicadas to Centrifuges - The Frugal Science Revolution
- Glowing Vomit, Cricket Serenades
- Guardian of the Wild - A Veterinarian's Story
- In the Swarm's Shadow - A Tale of Locusts
- Living With a Stone Age Brain
- Living in Extreme Worlds
- Lizard Push-ups and Jumping Spiders
- Making Life Happen
- Monkey Tales - Learning About Stress
- Next Gen Scientists
- Our Amazing but Flawed Memory
- Robot Snakes and Jumping Jerboas
- SLEAP and the Science of Movement
- Secrets of the Honeybee
- Shark Tales
- Surprised at the Science Conference
- The Big Leap
- The Last Stand for Ice
- The Maddest Match Around
- The Secret Scientist
- The World’s Deadliest Animal
- Tiny Versus Mighty
- What Makes You, You?
- What’s Been Cooking at SICB
- Zoo Animal Fun, Games, and Wellbeing
- Are Your Cells Cooperating or Cheating?
- Beetle X-rays
- Break Proteins in Eggs
- CRISPR Science
- Clawed Climbers?
- Exploring the Dark Side of the Earth
- High Flying Science
- History, Rabbits, and a Deadly Virus
- Honey Bee Waggle Dance
- Leafcutter Ant Life
- Learning from Darwin's Finches
- Life 3.0
- Life in the Cold
- Microbes Living Inside Us
- See DNA
- Superoxide, Superhero, or Supervillan?
- Tiger Beetle Observations
- Virus Quest
- Why We Get Sick
- Life & Building E.T.
- Looking into Lucy
- Make Your Own Pocket Seed Viewer
- Math Biology
- Micronauts and beyond
- Monster DNA
- Mysterious World of Dr. Biology movie
- Mystery of the dying coral reefs
- NSDL
- New Species
- Ocean Winds and Climate
- Oh No-Exercise
- One Wormy World
- Ouch! Body defense and repair
- Panda-monium
- Plant Detective
- Pollen
- Putting the Touch into Biology
- Queen Switcharoo
- Rebooting the Immune System
- Roses Are Red, But Why?
- Science-Powered Games
- Secret Life of the Natural History Museum
- Skeleton Secrets
- Skin
- Social Nature
- Sounds of Nature
- Space Physiology
- Spider-Man
- Soil & Microbes
- Spiderwoman
- Stinging Mystery
- Strange Cricket Silence
- Stressed out
- Swarm Science
- Tales of Termites
- Talking Science
- Time Traveling Paleoentomologist
- Tiny Matter
- Tiny Tigers
- Ugly Bug Contest 2008
- Ugly Bug Contest 2009
- Ugly Bug Contest 2009 Winner
- Ugly Bug Contest 2010
- Ugly Bug Contest 2010 winner
- Ugly Bug Contest 2011
- Ugly Bug Contest 2011 winner
- Ugly Bug Contest 2012
- Ugly Bug Contest 2012 winner
- Ugly Bug Contest 2013
- Ugly Bug Contest 2013
- Ugly Bug Contest 2013 winner
- Ugly Bug Contest 2014
- Ugly Bug Contest 2014 Winner
- Ugly Bug Contest 2016
- Venom!
- Visit to the Plankton Zoo
- Watching Grass Grow
- Why Is Life the Way It Is?
- Wickedly Cool Plants
- Young Women in Science Part 1
- Young Women in Science Part 2
- Zombie Ants
- PLOSable Biology
- A Warmer Future for National Parks?
- A Win-Win with Wind
- Aerial Ant Acrobatics
- Always Judge a Grouse by its Cover
- Amoeba Families Stick Together
- Are Plankton Ocean Super Stars?
- Batty for Food
- Benefits of Being Choosy
- Birds of a Feather Change Together
- Blurring the Line Between Plants and Animals
- Brain Food
- Brain-to-Brain Instant Messaging
- Bumblebees: Simple Creatures or Great Teachers?
- Cancer Cells on the Move
- Choosing Words Wisely
- Colorful Copycat Frogs of Peru
- Combining Senses
- Coping with Parasites in a Wild World
- Decoding Emotions in the Brain
- Diabetes Protein Puzzle
- Do You Have a Caveman's Brain?
- Does Playing Music Reduce Stress?
- Doggie Diversity
- Eat More, Sleep More
- Feeding the Beast: How Germs Eat for You
- Fish Out of Water
- Fishy Vanishing Act
- Flight of the Bumblebees
- For Teachers
- Foraging in the City
- Fountain of Youth
- Friend or Foe: Fish Facial Recognition
- Game On!
- Give Your Brain a Break
- Giving Bees a Sweet Tooth
- Half Man, Half Machine: Becoming Robotic
- Hey, I Know You!
- How Stem Cells Affect Cancer
- Hungry Mosquito Habits
- I Spy With My Little Eye
- If You Give a Mouse McDonalds
- Is It Easy Being Green?
- Is a City Slicker Sicker?
- Isn't It Ionic?
- Jaws of Death: When Plants Bite Back
- Jumping Genes of the Kangaroo
- Larval Beetles Spin Their Wheels on the Beach
- Lazy Eyes Hard at Work
- Looking for E. T.
- 'Sleeping' Viruses
- Between Bat Brains
- Can City Ants Handle City Heat?
- Cells Divide to Stay Alive
- Defending Desert-dwellers
- Does Science Support Social Distancing?
- Fly Immune Issues in Space
- Foxfire's Ghostly Call
- Hunting for deadly bacteria
- Learning Science With the Hobbits
- Local Fly Food Secrets
- Rethinking Sharks
- Seedy Secrets in Primate Poop
- Shorter Winters and Wolf Leftovers
- Where Did the SARS Coronavirus Come From?
- Angiosperms: A Guide to World Domination
- Bacteria and Fungi Battle On Bat Skin
- Is The Letter 'A' Red?
- It's Raining Cats and Dogs... and Mushrooms
- Mischievous Microbes
- Shape-shifting Brain Cells
- Sugary Surprises of RNA
- Ants Can Feed Plants
- Bacteria in the Belly of the Bee
- Body Fat May Trick Your Tastebuds
- Brains and Pain: Predicting Responses
- Can Marine Algae Change with the Climate?
- Countdown to Disaster in Marine Food Webs?
- Fatty Foods May Lead to a Leaky Gut
- Fossils Rewrite History
- Hot Flashes in the Ocean
- Making Medicine from Mushrooms
- Plant and Microbial Invasions
- Should Science Teachers Try to be Funny?
- Spicy is Tasty to Tree Shrews
- Tick Bacterial Trick
- When Great Apes High-Five
- Motions of Magic
- Nature's Balancing Act
- New World Under the Sea
- Of Mice and Men: Using Mice to Study Human Brains
- One-Two Punch for Tuberculosis
- Organ Swap
- Our Bodies, the Tumor Feeders
- Planting Pollinator Grocery Stores
- Prey Pretend to be Predator
- Proof Is in the Poop: What Neanderthals Ate
- Ranked and Ready : The Most Important Diseases To Study
- Rare Species Work Hard
- Robo-Mutants!
- Science of Teamwork
- Shimmery Defense
- Sleeping Secret Behind Bullying Behavior
- Speed of the Human Brain
- Spies Among Ants
- Spreading Stories of Sickness
- Students, Brains, and Science
- The Nose Knows
- The Push for Perfection in Breast Cancer Screening
- The Tadpole or the Egg?
- Think Fast!
- Tigers are Grrrrreat!
- To Grow or Not to Grow GMOs
- Trees Get By with Ant Aides
- Trouble in the Tropics
- What’s the Link Between Music and Your Brain?
- When Ecosystems get Fishy
- When the Flu gets Cold
- Where Are the Insects?
- Who Needs Sleep Anyway?
- Why Are Our Arms the Same Length?
- Why Did the Turtle Cross the Road?
- Why Don't Woodpeckers Get Headaches?
- Zombie Ants
- Embryo Tales
- All About Autism
- Cells, Frozen in Time
- Confronting Human Chimerism
- Creating Chimeras
- Ectopic Pregnancy: An Unexpected Path
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Pregnancy
- Focusing on Female Infertility
- Gender Identities and Expression
- Gender versus Biological Sex: What’s the Difference?
- Getting to Know the Germ Layers
- Helpful Sex Hormones
- How Fast Do Embryos Grow?
- Introducing the IUD
- Investigating In Vitro Fertilization
- Menstruation Matters
- Periods: What Should You Expect?
- Shedding Light on Endometriosis
- Summarizing Sex Traits
- The Mysterious Case of the Missing Periods
- Twin Tales
- Understanding Intersex
- What Is the Menstrual Cycle?
- When Blood Types Shouldn’t Mix: Rh and Pregnancy
- Xs and Ys: How Our Sex Is Decided
- EvMed Edits
- Stories in Other Languages
- My ASU
- Colleges and Schools
- Map and Locations
- Directory
- Home
- Activities
-
Stories
- World of Biology
- Meet Our Biologists
- Listen and Watch
- PLOSable Biology
-
Embryo Tales
- All About Autism
- Xs and Ys: How Our Sex Is Decided
- When Blood Types Shouldn’t Mix: Rh and Pregnancy
- What Is the Menstrual Cycle?
- Understanding Intersex
- Twin Tales
- The Mysterious Case of the Missing Periods
- Summarizing Sex Traits
- Shedding Light on Endometriosis
- Periods: What Should You Expect?
- Menstruation Matters
- Investigating In Vitro Fertilization
- Introducing the IUD
- How Fast Do Embryos Grow?
- Helpful Sex Hormones
- Getting to Know the Germ Layers
- Gender versus Biological Sex: What’s the Difference?
- Gender Identities and Expression
- Focusing on Female Infertility
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy: An Unexpected Path
- Creating Chimeras
- Confronting Human Chimerism
- Cells, Frozen in Time
- EvMed Edits
- Stories in Other Languages
- Images
- Links
- Contact
- About
show/hide words to know
Satiety: the state of being fed or full.
Taste Receptors You Can’t Taste
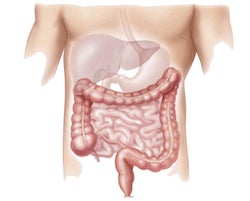
Our digestive tracts also have taste receptor cells. Image by www.cancer.gov(link is external)
Research in the last decade has found that taste receptor cells are not actually confined to the oral cavity. These cells are also found in the digestive tract and pancreas, but instead of signaling a perception of taste to the brain, they sense nutrients in the body, and adjust the secretion of metabolic hormones. The circulation of these hormones helps to regulate appetite and satiety (fullness), as well as glucose (sugar) levels in the bloodstream.
Animals, Taste, and Evolution
Most animals have taste receptors similar to ours, but the types they have and the location tends to relate to the lifestyle of the animal. Cats, for instance, and other carnivores, do not have sweet taste receptors. Because their diet is very low in carbohydrates and high in protein, they have lost the ability to taste sweet through evolution. Most whales and dolphins have actually lost almost all taste receptors. They swallow their prey whole, and therefore have no need for a sense of taste. Fish, on the other hand, have taste receptors all over their body, including their skin, gills, and lips. This allows them to find food suspended in the water.
Additional images via Wikimedia Commons. Cat licking paw by torbakhopper.
Read more about: How Do We Sense Taste?
View Citation
Bibliographic details:
- Article: Taste Outside the Mouth
- Author(s): Shelley Valle
- Publisher: Arizona State University School of Life Sciences Ask A Biologist
- Site name: ASU - Ask A Biologist
- Date published: October 6, 2017
- Date accessed: January 10, 2025
- Link: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/taste-outside-mouth
APA Style
Shelley Valle. (2017, October 06). Taste Outside the Mouth. ASU - Ask A Biologist. Retrieved January 10, 2025 from https://askabiologist.asu.edu/taste-outside-mouth
Chicago Manual of Style
Shelley Valle. "Taste Outside the Mouth". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 06 October, 2017. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/taste-outside-mouth
MLA 2017 Style
Shelley Valle. "Taste Outside the Mouth". ASU - Ask A Biologist. 06 Oct 2017. ASU - Ask A Biologist, Web. 10 Jan 2025. https://askabiologist.asu.edu/taste-outside-mouth
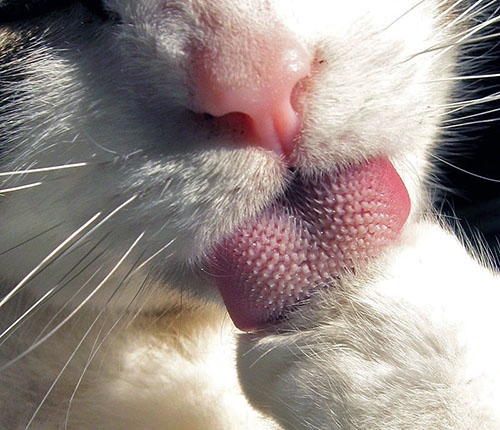

Most animals have taste receptors, but they do not have all the same ones as humans. For example, cats can't taste sweetness.
Be Part of
Ask A Biologist
By volunteering, or simply sending us feedback on the site. Scientists, teachers, writers, illustrators, and translators are all important to the program. If you are interested in helping with the website we have a Volunteers page to get the process started.







